
Pakauša kaula rievas Diagram Quizlet
groove for sig·moid si·nus. [TA] a broad groove in the posterior cranial fossa, first situated on the lateral portion of the occipital bone, then curving around the jugular process on to the mastoid portion of the temporal bone, and finally turning sharply on the posterior inferior angle of the parietal bone and becoming continuous with the.

(PDF) Spánková kost Os temporale · Os temporale. Neurocranium Processus mastoideus
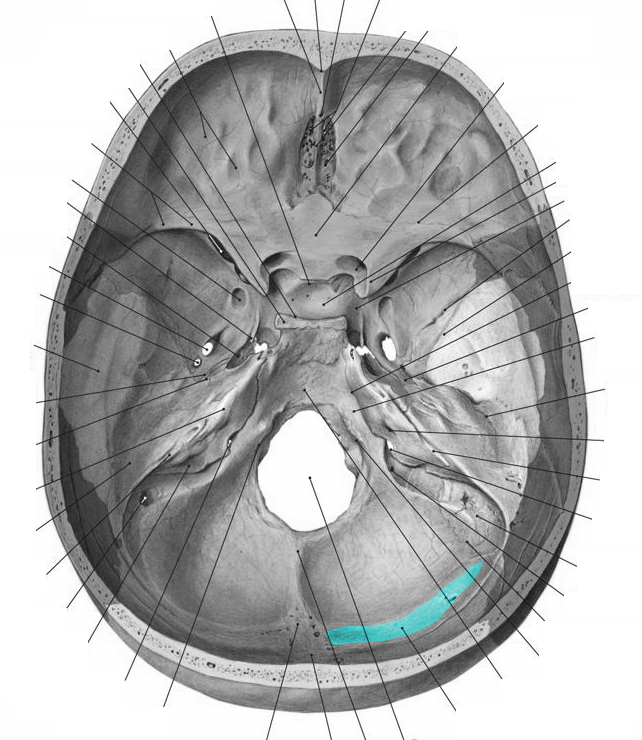
Sulcus sinus sigmoidei. Sulcus sinus petrosi inferioris (Os occipitale) Incisura jugulars (Os occipitalis) Sulcus sinus sigmoidei (Os occipitale) Uploaded by: rva Netherlands, Leiden - Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden University. Creator(s)/credit: Jānis Šavlovskis MD, PhD, Assistant Professor; Kristaps Raits, 3D generalist.

Fråga AnatomiHuvud Hals Os Occipitale 3 (Läkarprogrammet > Termin 2 > NOR > Anatomi
Sulcus sinus petrosi inferioris - Groove for inferior petrosal sinus Porus et meatus acusticus internus - Internal auditory porus & meatus Apertura externa aqueductus vestibuli - External opening of vestibular aqueduct Sulcus sinus sigmoidei - Groove for sigmoid sinus Fissura orbitalis superior - Superior orbital fissure

Occipital bone
The list of terms: Cellulae mastoideae within the semi-transparent temporal bone. The lateral projection. The complex view of some major internal structures of the temporal bone, including mastoid cells (yellow), the facial canal (green), labyrinth (red), tympanic cavity with canalis musculotubarius (magenta), and meatus acusticus internus (blue).

Parietal bones
The sulcus sinus sigmoidei is formed by the sinus sigmoidei. This is a venous blood stream near the occiput. It is S-shaped and supplies the brain with important messenger substances. The sigmoid sinus is responsible for both supply and removal of the cerebral blood. Many other veins arise from it.

Os parietale, facies interna Diagram Quizlet
Sigmoid sulcus The inner surface of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone presents a deep, curved groove, the sigmoid sulcus, which lodges part of the transverse sinus; in it may be seen the opening of the mastoid foramen . References This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 142 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)

Sigmoid sinus Medical textbooks, Medical anatomy, Ear anatomy
Superior sagittal sinus (sulcus sinus sagittalis superioris) Along this groove, there are granular foveolae (foveolae granulares). These are traces of formations of the cranial arachnoid mater. Granular foveolae (foveolae granulares) In the area of the mastoid angle lies the groove for the sigmoid sinus (sulcus sinus sigmoidei).

Sigmoid sulcus Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
Sulcus sinus sagittalis superioris (midline groove for the superior sagittal sinus) Sulcus sinus sigmoidei (part of the groove for the sigmoid sinus) Cranial sinuses - brain-drains. A cranial sinus or dural venous sinus is a space that absorbs blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Sinuses empty into larger veins that return these fluids to the.

Perpetuu BAC Confuz lamina cribrosa craniu A indrazni metropolitan bicicletă
Sigmoid sinus (Sinus sigmoideus) The sigmoid sinus is a paired intracranial venous channel. It arises from the transverse sinus at the level where the transverse sinus leaves the tentorium cerebelli.The sigmoid sinus courses along the floor of the posterior cranial fossa to enter the jugular foramen.It drains into the jugular bulb via which it connects with the internal jugular vein.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/crista-galli-2/fW6CjbHnMnF1Rhfg8MkJNg_Crista_galli_01.png)
Palatine bone Anatomy, borders and development Kenhub
The base of the occipital bone articulates with the first cervical vertebra - or C1 - thanks to the condylar part of occiput that anatomically ressambles the processus articularis inferior of cervical vertebra. The reason behind this is the common somatic origin of the occipital bone and vertebral column.

Parietal bone. External surface Anatomy bones, Muscle anatomy, Human anatomy
The sigmoid sinuses (sigma- or s-shaped hollow curve), also known as the pars sigmoid, are paired dural venous sinuses within the skull that receive blood from posterior transverse sinuses . Structure The sigmoid sinus is a dural venous sinus situated within the dura mater.
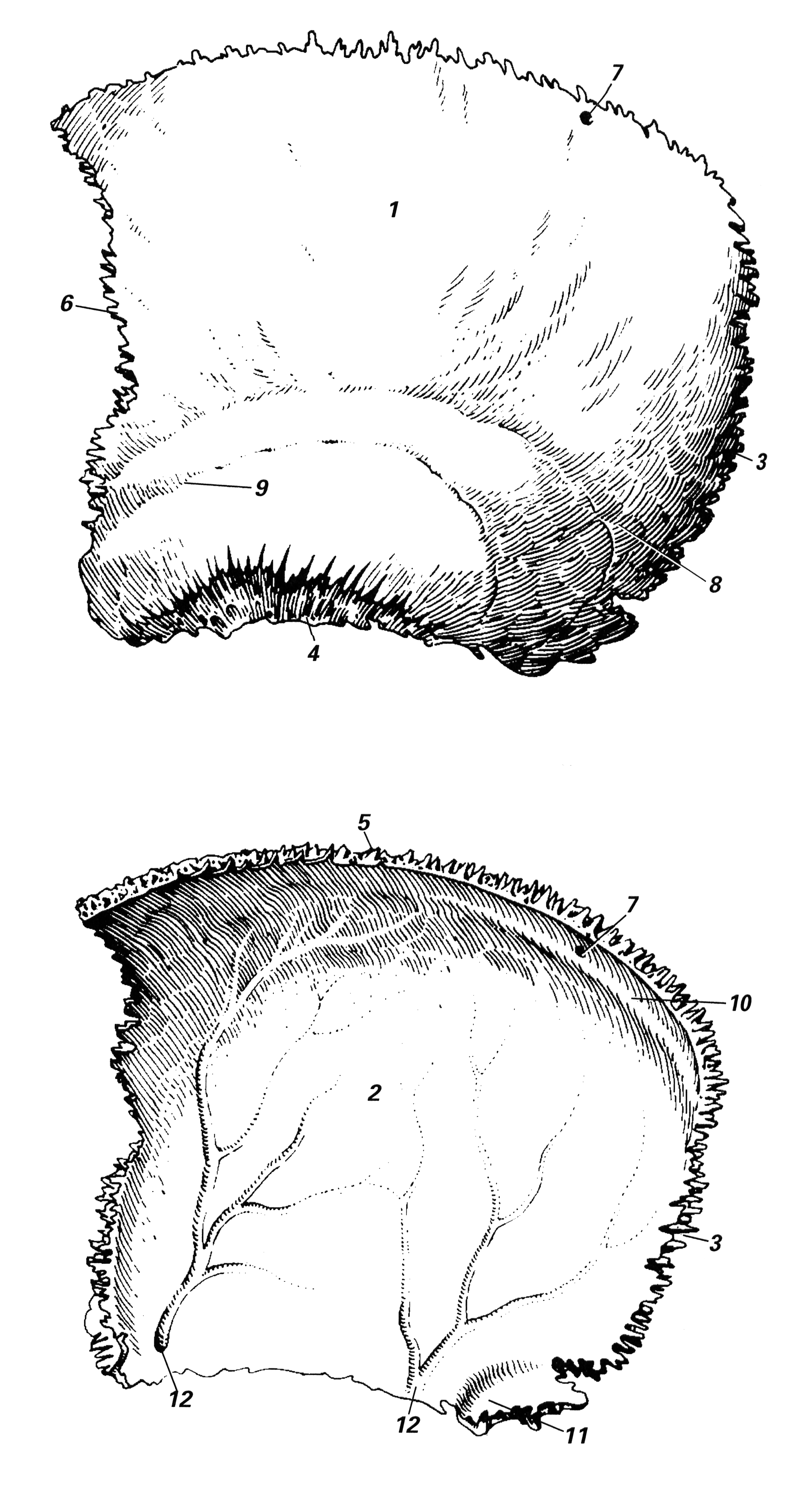
Затылочная кость рисунок 44 фото
The sigmoid sinus (plural: sigmoid sinuses) is a paired structure and one of the dural venous sinuses. It is the continuation of the transverse sinus (which is similarly variable in size) and becomes the sigmoid sinus as the tentorium cerebelli ends. It is here that the sinus receives the superior petrosal sinus.
Level 12 Gelenke, Knochenpunkte etc, Memrise
The Sulcus sinus sigmoidei is located in this. The sulcus sinus sigmoidei is formed the sinus sigmoidei. This is a venous bloodstream near the occipital bone . It is S-shaped and supplies the brain with important messenger substances . The sigmoid sinus is responsible for both the supply and the removal of cerebral blood. Many other veins.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/glandula-pituitaria-3/O8Hpr8OcMIWkBVRTVi86nw_Hypophysis_01.png)
Diencéfalo Anatomia, Estruturas e Funções Kenhub
Sulcus sinus sigmoidei - Groove for sigmoid sinus Anterior aspect of two parietal bones with some distance between them. The list of terms: Tuber parietale - Parietal tuber Sulcus sinus sagittalis superior - Groove for superior sagittal sinus Sulcus.

Inversoul adlı kullanıcının Anatomy Osteology Human panosundaki Pin, 2020
Groove for Sigmoid Sinus is a groove in the posterior cranial fossa. [1] It starts at lateral parts of occipital bone, curves around jugular process, and ends at posterior inferior angle of parietal bone. After that, groove for sigmoid sinus continues as groove for transverse sinus. [2] See also Sigmoid sinus References

The Skull
The relationship of the mastoid air cells to the sulcus was analysed and air cells were found just behind the sulcus in 66% and behind and posterior to the sulcus in 5% of temporal bones.RésuméLes variations de taille et de forme du sillon du sinus sigmoïde et ses rapports avec les structures adjacentes furent étudiés sur 531 os temporaux.